From tuition to takeaways, why China’s regulatory crackdown is proving unappetising for investors
China’s government has just provided investors with another reminder of why they should tread carefully when putting money into the country.
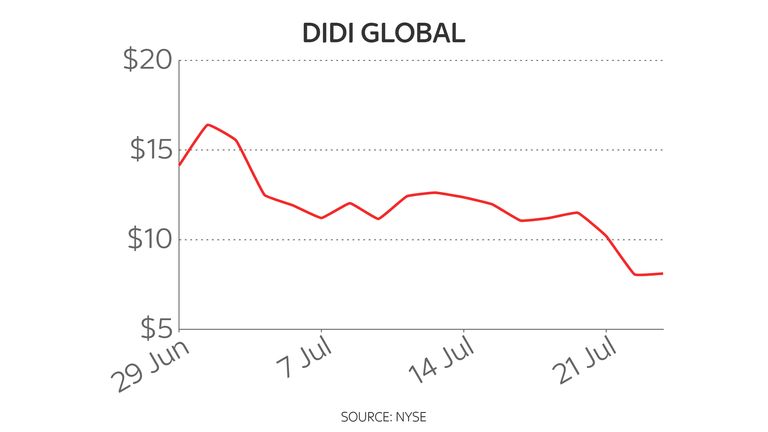
At the end of last month, the Chinese ride-hailing app Didi made history when it floated on the New York Stock Exchange with a valuation of $70bn, making it the biggest IPO of a Chinese company in seven years.
Just days later, the Chinese government told Didi to stop registering new drivers and users for its app, which it followed by demanding that Didi be removed from Chinese app stores.
The shares plunged and are now 42% lower than the price at which they listed.
Now Beijing has done it again with a fresh salvo aimed at tech and education companies.
Firstly, the Chinese government announced on Friday night that it was banning private tutoring and test preparation for core school subjects, arguing the move would ease financial pressure on hard-up Chinese families.
Private tutoring in China is a $120billion-a-year business and around three-quarters of Chinese children are reckoned to have some form of private tuition outside school.
Beijing, which is concerned about the country’s rapidly-ageing population, suspects the financial pressure of educating children privately may be a reason why couples are still not having more children despite the abolition in 2015 of the “one child” policy.
The measure, which is believed to have come from President Xi Jinping himself, was accompanied by restrictions on foreign investment in private tutoring companies and is also expected to see advertising bans imposed – as well as restrictions on when tutoring can be made available.
The move sent shares of private tuition companies, many of which are listed in Hong Kong, tumbling.
New Oriental Education & Technology finished the session down 47%, while Scholar Education fell by 45% and Koolearn Technology by 33%.
Next came an attack on Tencent, one of China’s biggest tech companies, which on Saturday was ordered to give up the exclusive music licensing agreements it has signed with record companies – including Universal Music and Warner Music – around the world.
Tencent, which owns China’s most popular messaging service WeChat, is estimated to have an 80% share of the exclusive music streaming market in the country.
Shares of Tencent fell by almost 8% on the news.
Then, Beijing unveiled measures aimed at cooling what it sees as an overheated property market.
The People’s Bank of China (PBoC) is reported to have ordered lenders to raise mortgage rates for first time buyers from 4.65% to 5%.
At the same time, the PBoC is said to have ordered an increase in the interest rate for people buying second homes from 5.25% to 5.7%. That sent shares in property development companies lower.
Separately, China also today announced new rules aimed at better protecting delivery riders, following complaints that some are not being paid the minimum wage or are being sent on routes where it is impossible to complete the order in the time allowed.
That news sent shares of Meituan, one of China’s biggest food delivery companies, down by 14%.
Its shares have now halved in value since February.
Shares of the e-commerce giant Alibaba, which also operates a popular delivery service called Ele.me, fell by more than 6%.
Taken together, the various measures add up to an unappetising cocktail for investors, who reacted accordingly.
In Hong Kong, the Hang Seng slid by 4.13%, taking it to a level not seen since December last year.
In Shanghai, the blue-chip CSI300 index fell by 3.22%, again wiping out all gains for the year to date.
The broader Shanghai Composite, meanwhile, fell by 2.34% to a two-month low.
There are two schools of thought as to what Beijing is doing here.
One is that this is just part of a wider campaign by the Chinese Communist Party to reassert its influence over life in China and strengthen its hand – with businesses and investors merely being caught up in this.
The other argues that this is a specific set of measures aimed at clipping the wings of businesses amid concerns that too many of them are not always operating within the law.
Aside from complaints about the treatment of workers in delivery firms, there is also a sense that the accounting practices of some property companies many not stand up to scrutiny, that the banks are being too lax with their lending standards and that the wealth being created by some of these companies, particularly those in the tech sector, are being too concentrated among a handful of plutocrats.
That theory is given credence by, for example, the way Beijing scuppered last year’s proposed stock market flotation of the payments company Ant Financial, which would have further added to the wealth of Jack Ma, the billionaire entrepreneur that created Ant and its former parent company, Alibaba.
Concerns about the quality of accounting at some companies have been rumbling ever since a former stock market darling, the coffee shop operator Luckin Coffee, collapsed last year after falsifying its accounts.
Either way, investors have been spooked, although some will have only themselves to blame given the way regulatory risk in China has been overlooked in recent years.
But it has certainly prompted investors in China to look more closely at their portfolios as they try to assess what other companies are at risk of seeing their business models reduced to rubble overnight by regulators.
Rightly so.
This Chinese government is very different from its immediate predecessors and is clearly far more relaxed about alienating foreign investors if it considers more important principles are at stake.