‘There’s a stigma attached to going to work’: The 800,000 people who have fallen into ‘economic inactivity’
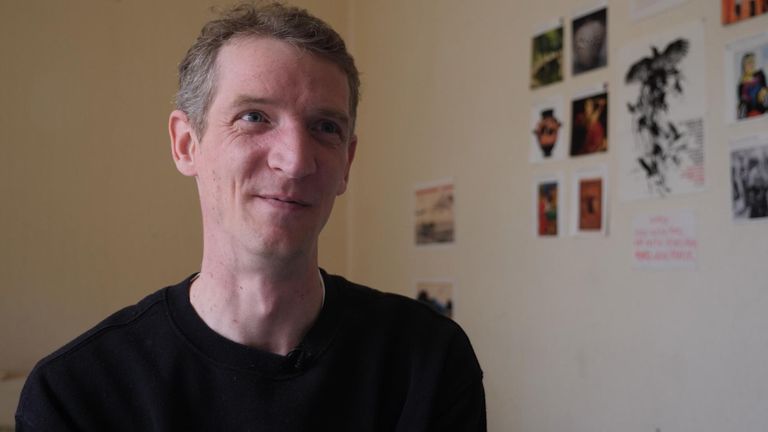
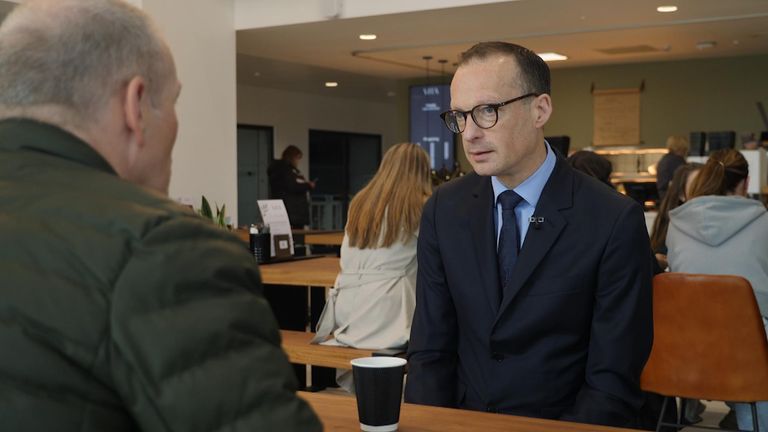
Michael is fair haired and frail, with a face that tells a story. Until seven years ago his life was perhaps as he imagined it. He was married and working for a fancy food shop in his home town in North Yorkshire.
Then something happened. He is reluctant to share the full details but his marriage broke down, he lost the job, and was left with a choice: “It was to be homeless, or move to a bedsit in Middlesbrough,” he says.
Which is how we come to be speaking in the Employment Hub on Corporation Road, opposite Middlesbrough’s Jobcentre.
A council-backed centre, it offers help and guidance to anyone looking to get back into work.
Young adults making the leap from education to employment; older people who want or need to earn again; and clients like Michael, who fall somewhere in between, derailed by illness or personal circumstances.
‘I’ve lost my confidence’
He has not worked for six years and he’s here to try to change that. “With not being in work for a while I’ve lost my confidence,” he says.
“I got stuck in a routine and I’m not the best at helping myself out at times. You feel like you’re stuck. It would be nice to get back into a work routine. You feel better in yourself through having a job.”
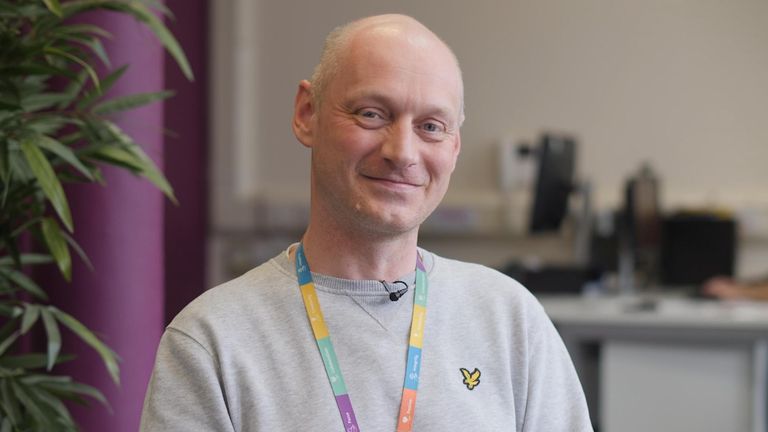
Michael has an appointment with Doug Hewitson, once long-term unemployed himself. He points clients towards an array of services they might need to help them work, from compiling a CV and getting basic qualifications, to training and work experience opportunities.
“We primarily work with retirees, the short-term sick and people with young families, that tends to be with children younger than two,” Doug says. “Generally, they will be on a type of universal credit that doesn’t have the requirement to seek work attached to it. And we have a lot of them.”
The Employment Hub is trying to help fill a gap that exists across the country as the economy struggles with a labour market crisis that has nothing to do with the number of jobs.
Unlike the unemployment crisis of the 1980s, there are plenty of opportunities, close to a million vacancies at the most recent count. The problem is finding people to fill them.
Since the pandemic almost 800,000 people have fallen out of employment into “economic inactivity”, a catch-all definition that covers the nine million people of working age not currently able or looking to work.
That includes students, early retirees and stay-at-home parents and carers, but the largest and most pernicious reason is long-term sickness, which now accounts for more than 2.5 million people, an increase of more than 400,000 since COVID, driven largely by mental health conditions.
‘There is a stigma attached to going to work’
That has held back growth and pushed the welfare bill up, and the issue has gained political salience with Rishi Sunak characterising some mental health challenges as “the ups and downs of everyday life”.
Unemployment, inactivity and workless households are all above the national average in Middlesbrough and the Tees Valley but they are not unique.
“You can walk out on the High Street now and find several people who are economically inactive,” says Philip Bentham, who leads the employability team at housing association Thirteen in Stockton-on-Tees, which aims to help people into work.
“For some it’s health, mental health, low skills and qualifications, or generational unemployment. We’re working with families who are three and four generations unemployed within the household, mum and dad and grandparents that have never worked.
“Quite often there is a stigma attached to going to work. Their families are afraid of not having the safety net of the benefits system, and people sometimes sadly think work doesn’t pay. Our job is to convince them there is always something they can do.”
Read more:
Hopes for pre-election interest rate cut suffer further blow
The state response to worklessness is Universal Credit, a single payment that covers benefits for housing, children and childcare, as well as unemployment benefit, administered by the Jobcentre Plus network.
At Middlesbrough’s Corporation Road branch a steady stream of claimants arrive for their strict 10-minute appointments, watched by up to four security guards.
A mix of carrot and stick
In principle it’s a deal between the state and the claimant, a mix of carrot and stick. Claimants who can work are required to attend weekly meetings with a work coach and take steps to find a job. Fail to do this and you can be “sanctioned”, often by reducing cash payments.
If you are too sick to work however the requirement to look for a job falls away leading to the suspicion, apparently shared by the prime minister, that some claimants are citing mental health conditions to get signed off.
I ask work coach Michaela Fulleylove if some people do play the system.
“I’m saying yes, definitely. But we have to treat every individual with trust, fairness and compassion.
“But we have to be able to ask questions, because not only is it our job to support the public, we’ve also got to protect the public purse.”
For all the challenges in Middlesbrough and the Tees Valley there are opportunities.
The demise of ICI and British Steel, huge paternal employers that offered their own safety net, left a gap that has never been adequately filled.
The latest attempt is levelling up, largely channelled through the Tees Valley mayoralty of Ben Houchen.
Europe’s largest brownfield development, the controversial Teesworks freeport, is taking shape and there are advanced manufacturing opportunities in the renewable energy industry serving a huge new offshore wind project at Dogger Bank.
Thousands of jobs are promised, an incentive for the workforce and a challenge for employers.
AV Dawson has operated the Port of Middlesbrough in the shadow of the town’s landmark Transporter Bridge for 80 years.
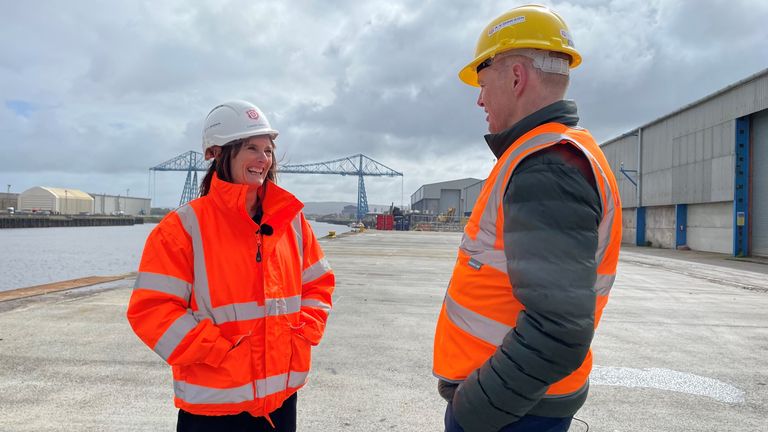
They employ about 200 staff and people and culture director Louise Croce tells me they have no problem filling roles or retaining staff.
‘We get people who want to be hairdressers applying to be forklift truck drivers’
She points out the perverse incentives of a benefits system that requires claimants to apply for jobs, irrespective of whether they can do them.
“We get people who want to be hairdressers applying to be forklift truck drivers. You do question whether some of it’s around their ability to claim benefits,” she says.
But those who do work for her receive a level of support, particularly around mental health, that would have been unimaginable in Middlesbrough’s macho industrial past.
“We provide a lot of support inside the company, we have health and well being ambassadors, because mental health is such an issue in the area. We try and look after people, help them with issues early, before they become a problem.”
On the edge of a city centre abandoned by big retailers is Teesside University, a cluster of new buildings that is evidence of badly needed investment.
The vast majority of the 20,000 students come from within a five-mile radius, and deputy vice chancellor Professor Mark Simpson tells me they aim to prepare them for the promised jobs, from digital and AI, health and life sciences, public sector jobs and the net zero industries.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free



“We work with businesses and we work with industry to look at demands, look at what skill sets they need from our graduates,” he says. “But we don’t just respond, through those clusters of courses we help create the industries.”
“But when you see the levels of deprivation across the Tees Valley a big part of what we need to do is raise aspiration.”